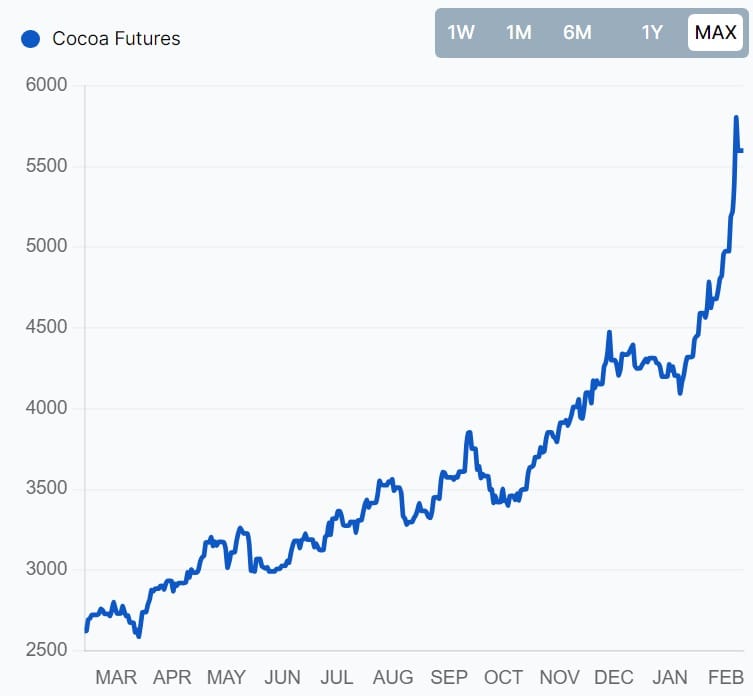
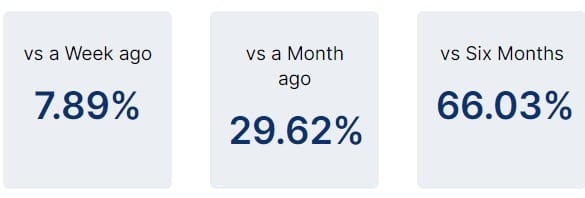
Cocoa Prices Up 66% in 6 Months

Cocoa prices are skyrocketing in response to inclement dry weather in West Africa (3/4 of global crops), with regions such as heavy producers Ghana and Ivory Coast taking the biggest hit, forcing a per metric ton all-time high nearing $6,000.
Confectioners such as Hershey in the US are feeling the crunch, reporting low double digit earnings decreases YoY.
Sweet Commodity at the Heart of Global Trade
Cocoa, derived from the cacao tree, is more than just a flavor; it's a commodity that fuels a multibillion-dollar industry and plays a vital role in global trade. From its cultivation in tropical regions to its transformation into various products, cocoa traverses a complex supply chain, influenced by factors ranging from weather patterns to geopolitical dynamics.
Sourcing and Cultivation
The cacao tree thrives in the humid tropics, primarily within a narrow belt of 20 degrees north and south of the Equator. West Africa, particularly Ivory Coast and Ghana, stands as the dominant producer, accounting for over two-thirds of global cocoa output. Other significant producers include countries like Indonesia, Ecuador, and Nigeria.
READ Silver Replacing Gold Among Egyptians as Alternative Store of Value
Cocoa cultivation is labor-intensive and typically involves smallholder farmers, who cultivate the trees on small plots of land. The process begins with the planting of cocoa seeds in nurseries, which are later transplanted to shaded areas within the farm. It takes several years for the trees to mature and start bearing fruit, known as cocoa pods, which contain cocoa beans surrounded by pulp.
Uses and Products
Cocoa beans are the primary raw material for chocolate production, but their applications extend beyond confectionery. Cocoa powder and cocoa butter, extracted from the beans, find their way into a myriad of products, including beverages, baked goods, cosmetics, and pharmaceuticals. The versatility of cocoa makes it a valuable ingredient in both food and non-food industries.
The Role of West Africa and Weather Patterns
West Africa's dominance in cocoa production is attributed to its favorable climate and abundant rainfall, which provide ideal growing conditions for cacao trees. However, the region is also vulnerable to weather-related risks, such as droughts and excessive rainfall, which can impact crop yields and quality. Climate change adds another layer of uncertainty, as unpredictable weather patterns threaten the stability of cocoa production.
In recent years, concerns have arisen regarding sustainability and ethical practices within the West African cocoa industry. Issues such as child labor, deforestation, and low farmer incomes have prompted calls for increased transparency and accountability across the supply chain. Initiatives like certification programs and industry collaborations aim to address these challenges and promote sustainable cocoa production practices.
Trading and Market Dynamics
Cocoa is traded globally on commodity exchanges, with London and New York serving as primary trading hubs. The prices of cocoa futures are influenced by various factors, including supply and demand dynamics, weather conditions, currency fluctuations, and geopolitical events. Speculators, hedgers, and institutional investors participate in the cocoa market, seeking to profit from price movements or manage their exposure to risk.
The cocoa supply chain involves multiple intermediaries, including farmers, cooperatives, exporters, processors, and manufacturers. Each stage adds value to the commodity, with prices fluctuating along the way. Transparency and efficiency in the supply chain are critical for ensuring fair compensation for farmers and maintaining the quality of cocoa products.
Cocoa stands as a quintessential commodity with a rich history and global significance. From its origins in tropical regions to its transformation into beloved treats and everyday products, cocoa embodies the complexities and interconnectedness of the modern global economy. As the industry grapples with sustainability challenges and market dynamics, stakeholders must collaborate to ensure the long-term viability and integrity of cocoa production and trade.
Want to be part of the data revolution? Join our Telegram to always be in the loop!

