2025 Economics Forecast: What Lies Ahead

2025 has arrived, and it’s set to be a crucial period for the economy. With Trump back in the Oval Office following Biden’s term, the administration faces some serious economic hurdles, such as persistent inflation and a ballooning public debt being two of the biggest.
Inflation is still running hot, leaving everyone wondering how long it will take to get back to that elusive 2% target. Will efforts be focused on solving inflation, or will 3% be the new 2%?
On top of that, addressing the growing public debt presents a complex and long-term challenge.
This article explores key forecasts for:
- Inflation
- Monetary Policy
- Economic Growth / Asset Prices
- Fiscal Policies
- Prediction Markets & Trump’s Administration
Inflation
Inflation rates are one of the most important indicators in an economy. Beyond reflecting the erosion of a currency's purchasing power, they guide monetary policy, which impacts economic growth.
2024 was characterized by a decline in inflation rates. However, the last few months revealed resilience in the downward trend.
For 2025, the challenge remains. Key factors to watch include the reduction in monetary policy restrictiveness and the potential imposition of import tariffs. Let’s take a look at what institutions are forecasting:
Survey of Professional Forecasters (Philadelphia Fed)
This survey is conducted quarterly and gathers projections from professional economists regarding inflation.
The data shows expectations ranging between 2.3% and 2.4% for the CPI and around 2.1% to 2.2% for the PCE by the end of 2025.
This indicates that experts believe inflation is unlikely to reach the 2% target in 2025.

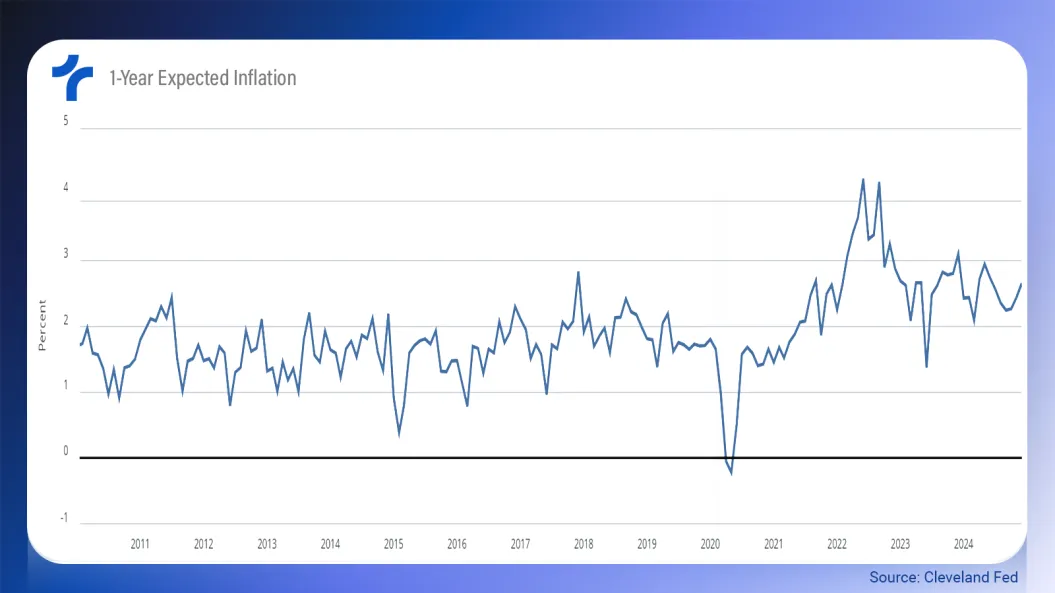
1-Year Expected Inflation - (Cleveland Fed)
This indicator from the Cleveland Fed generates an inflation expectation based on market prices such as Treasury yields, inflation data, inflation swaps, and survey-based measures of inflation expectations.
By analyzing premium differentials and the rates charged on bonds, the expected inflation rate among market participants is observed.
In December 2024, the indicator pointed to an inflation expectation of 2.64% one year ahead. Although this is lower than in December 2023, it was the highest figure since June 2024.
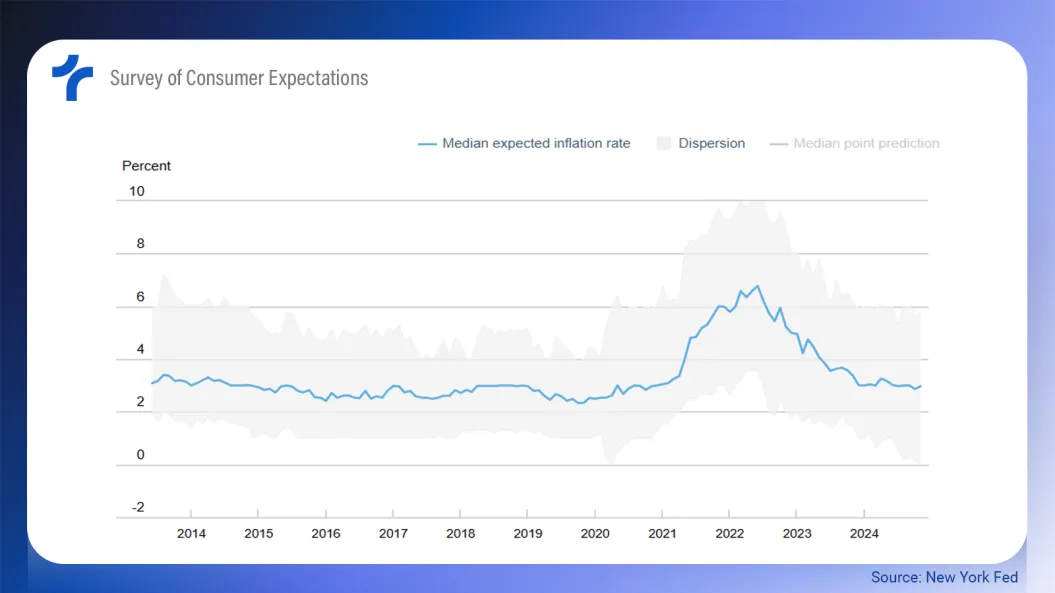
Survey of Consumer Expectations (New York Fed)
This survey considers consumer opinions. The latest survey, referring to November, reported a median inflation expectation of 3%.
Respondents are asked about their inflation expectations for 1, 3, and 5 years ahead.
In November, median inflation expectations increased by 0.1 percentage points (ppt) across all three horizons:
- 1-Year expectations rose to 3.0%.
- 3-Year expectations rose to 2.6%.
- 5-Year expectations rose to 2.9%.
Expectations from Major Banks
Leading financial institutions have also released their inflation forecasts for 2025.
- Bank of America: Inflation is expected to remain persistent. The core Personal Consumption Expenditures (PCE) index, the Federal Reserve's preferred measure, is forecasted to reach 2.8% by the end of 2025 and peak at 2.9% by the second quarter of 2026.
- J.P. Morgan: The 2025 economic outlook predicts a decline in global inflation, with the Consumer Price Index (CPI) expected to decrease from 3.0% to 2.7%. This suggests a gradual easing of inflationary pressures, though disinflation rates may vary across regions.
- Goldman Sachs: U.S. core PCE inflation is projected to decrease to 2.1% by the end of 2025, excluding potential tariff impacts. However, anticipated tariff increases on imports from China and automobiles could push the rate to approximately 2.4%, reflecting a one-time price adjustment.
Monetary Policy
After a 100 basis point reduction in 2024, additional cuts to the Fed Funds rate are expected in 2025.
The key question is how much inflation will allow for further rate cuts. By the end of 2024, the CPI showed a slight increase, which may suggest that a less restrictive policy might not be sufficient to control prices.
Major banks were expecting:
- Bank of America: Anticipates the Federal Reserve will implement two interest rate cuts during this cycle—in March and June—reducing the terminal rate to a range of 3.75% to 4%.
- J.P. Morgan: Expects the Fed to lower interest rates by 100 basis points, bringing the rate down to 3.75%. This monetary policy adjustment is intended to support economic growth while keeping inflation in check.
- Goldman Sachs: Forecasts a gradual series of interest rate cuts beginning in 2025, with the following timeline:
- March 2025: An initial cut of 25 basis points.
- June 2025: A second cut of 25 basis points.
- September 2025: A final cut of 25 basis points.
These adjustments were projected to lower the Federal Funds rate to a range of 3.5% to 3.75% by the end of September 2025. However, after the employment data of January 10th:
- Goldman Sachs: Revised down to 2 rate cuts this year, beginning in June 2025
- Bank of America: Rate cuts no longer expected in 2025, rate hikes more likely than cuts
- JP Morgan: Revised down to 2 rate cuts this year, beginning in June 2025
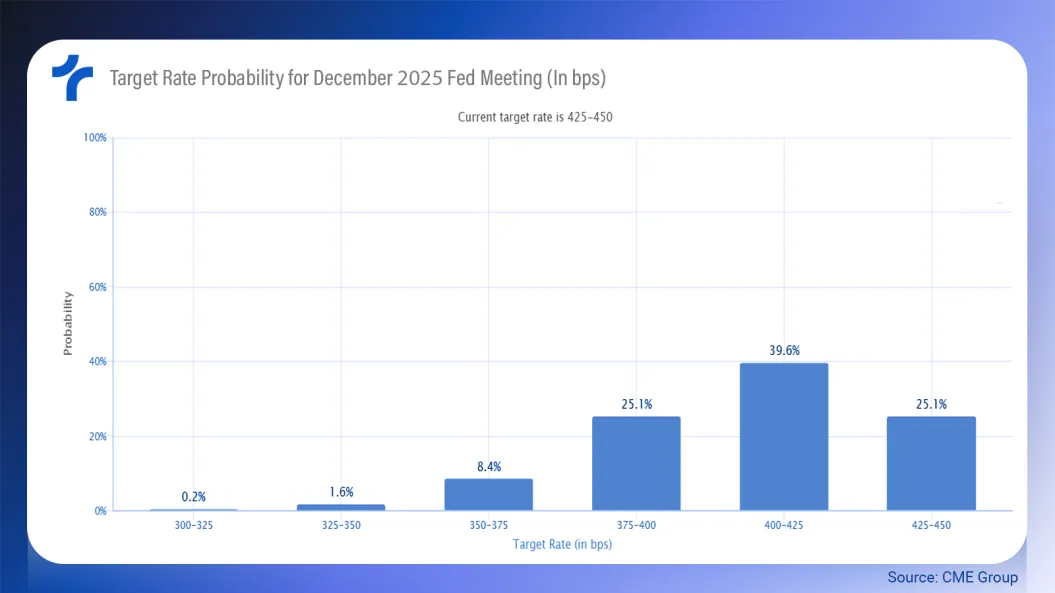
On the other hand, market traders point out that there is a lower probability of this happening, according to the contracts negotiated the expectation is that the greatest chance is of an interest rate between 400 and 425 bps in December 2025.
With more than a 90% chance of being in a range above 375 bps.
The methodology used by the CME Group analyzes the probabilities of possible Fed Funds target rates based on Fed Funds futures contract prices.
Economic Growth and Financial Markets
Asset prices are heavily influenced by economic growth, which impacts projections of future cash flows.
Economic growth is essential not only for assets but also for maintaining and improving the population's quality of life and keeping the debt-to-GDP ratio stable.
Check out some projections for U.S. GDP in 2025.
- Bank of America: Projects stable economic growth, with GDP increasing to 2.5% in the first quarter and averaging 2.3% for the year.
- J.P. Morgan: Forecasts a moderation in GDP growth, slowing from 2.4% to 2.0%, signaling a deceleration in economic expansion.
- Goldman Sachs: Predicts U.S. GDP will grow by 2.5% for the full year.
Asset Prices
The main indices and assets to be analyzed are the S&P 500, DJIA, NASDAQ, Gold, and Bitcoin.
Sources will include major financial institutions and influential figures in the field.
Overall, expectations appear to be optimistic.
S&P 500
- Goldman Sachs: Targets 6,500, suggesting around 9% price gain.
- Deutsche Bank: Projects a more optimistic 7,000.
- BofA: Expects the index to reach 6,666.
NASDAQ & DJIA
- Wedbush Securities: Analyst Dan Ives anticipates a 25% surge in the NASDAQ, driven by AI advancements and favorable Trump-era regulations.
- Traders Union: Forecasts DJIA at 49,867 by end-2025, with further growth to 51,423 by 2029.
Bitcoin
- Bitwise: Predicts $200,000.
- Robert Kiyosaki: Forecasts between $175,000 and $350,000.
- Matthew Sigel (VanEck): Projects $180,000.
- James Butterfill, CoinShares: While acknowledging the possibility of Bitcoin reaching $150,000 in 2025, Butterfill also warns of a potential correction down to $80,000.
Gold (per ounce)
- JP Morgan & Goldman Sachs: Both project $3,000.
- InvestingHaven: Predicts $3,275 in 2025, with a long-term forecast of $5,150 by 2030.
Fiscal Policy
Controlling government spending is one of the main challenges for the new president, especially as it requires political coordination.
Managing government expenditures is a difficult but necessary task. The current situation is problematic:
- Debt Ceiling: The U.S. is nearing its debt ceiling, requiring congressional action to avoid default. Despite a Republican-controlled government under President-elect Donald Trump, internal party disagreements on spending policies could delay a resolution. Fitch Ratings has raised concerns about governance issues affecting a swift agreement.
- Tax Policy: Senate Majority Leader John Thune acknowledges the significant national debt and suggests that upcoming GOP tax cuts may not be fully offset. The plan to extend the 2017 tax cuts could add $3.59 trillion to the deficit between 2025 and 2034. Thune highlights the importance of economic growth and spending reductions to achieve fiscal stability.
The Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE), tasked with identifying wasteful spending and harmful regulations, offers promise. However, its recommendations, expected in 2026, address only part of the broader fiscal challenge.
Combining DOGE's executive-focused efforts with a congressionally authorized fiscal commission to advance legislative changes could create the political momentum necessary to tackle difficult reforms, particularly in entitlement programs.
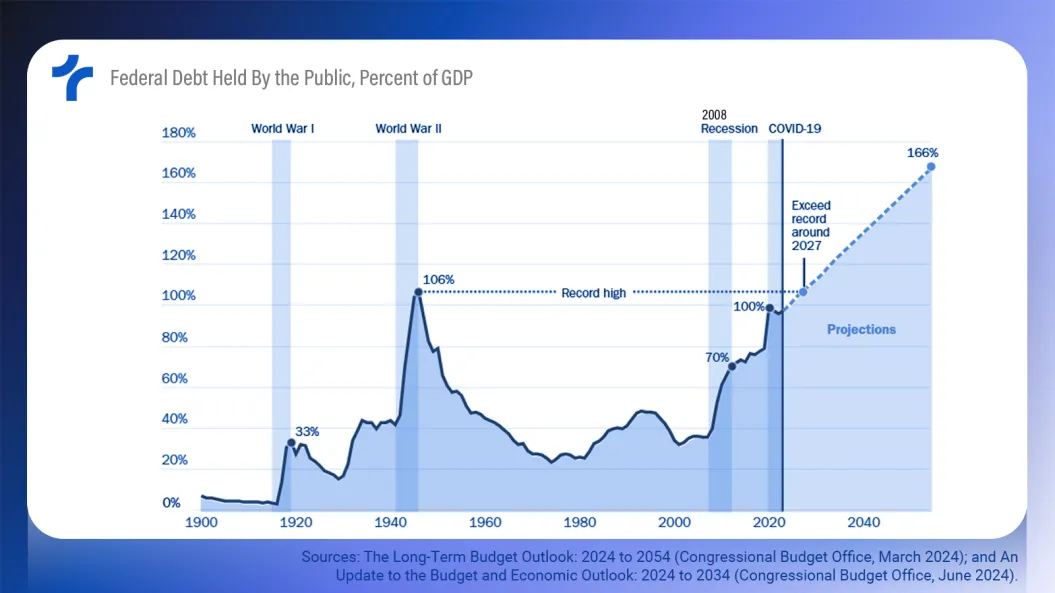
According to Fitch Ratings, the U.S. (AA+/Stable) faces significant fiscal policy challenges in 2025, including the debt ceiling, appropriations, and tax cut extensions, all against the backdrop of large deficits and a growing debt burden.
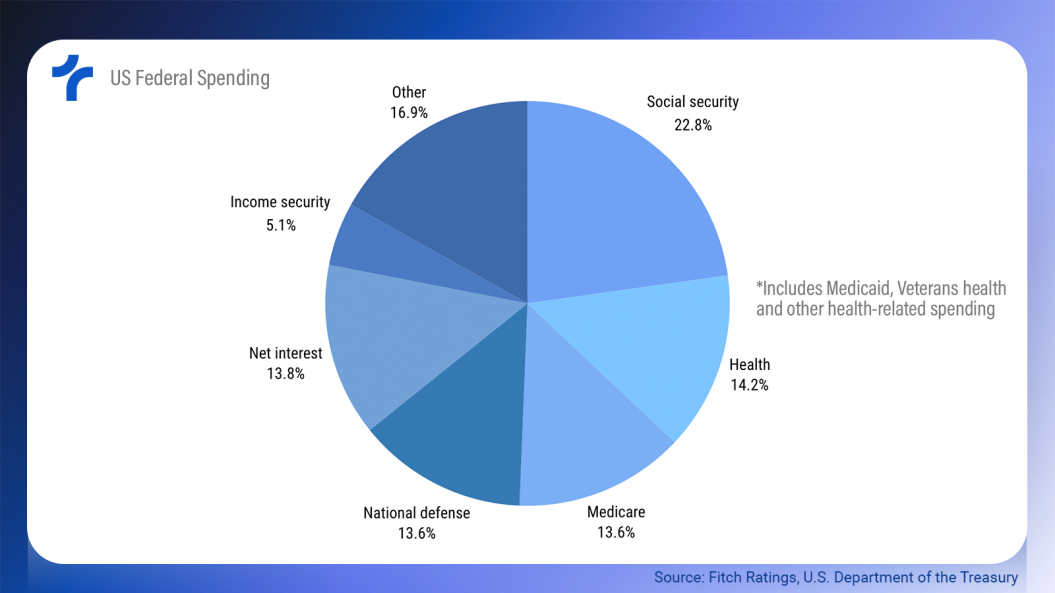
Fitch projects general government (GG) deficits to exceed 7.5% of GDP in 2025 and 2026, despite resilient GDP growth and cyclical revenue gains from personal and corporate taxes, strong 2024 stock market performance, and additional tariff revenues.
Deficits of this magnitude would drive GG debt above 120% of GDP by 2026, more than double the median for the ‘AA’ rating category.
While the Republican rhetoric emphasizes controlling spending, it remains to be seen how this will play out in practice.
Trump Administration
There is a certain expectation about what Trump will or will not do in his administration, especially regarding tariffs and public debt.
One way to estimate the probabilities is by resorting to Prediction Markets, which have already proven to be very effective during the presidential elections.
Public Debt
One of the main challenges is effectively controlling the public budget.
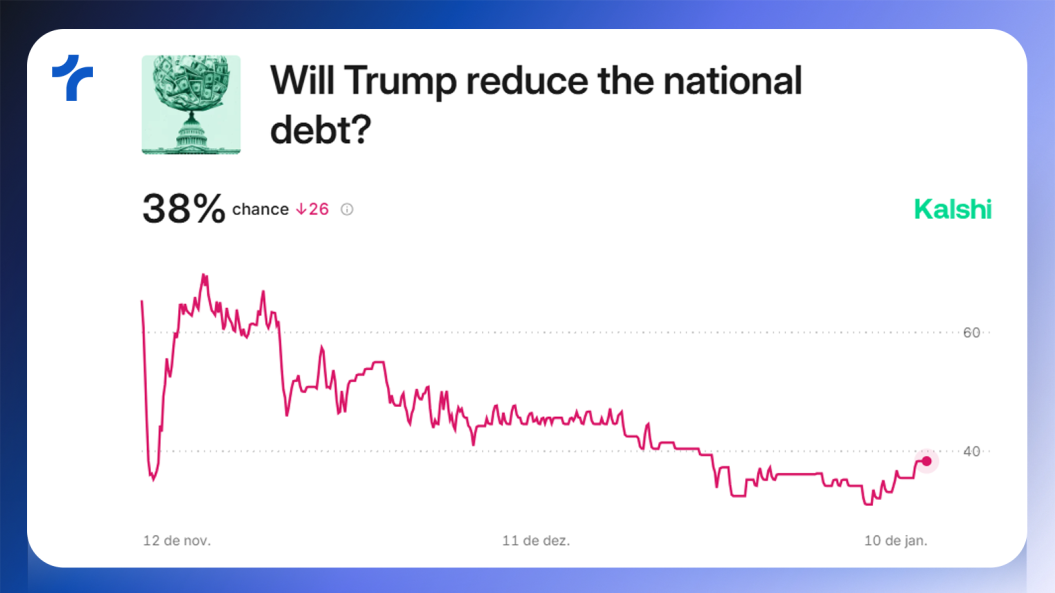
Right after the elections, Kalshi indicated a probability of over 60% that Trump would reduce public debt.
By early January, this probability dropped to below 40%, largely influenced by Trump's own statements.
Tariffs
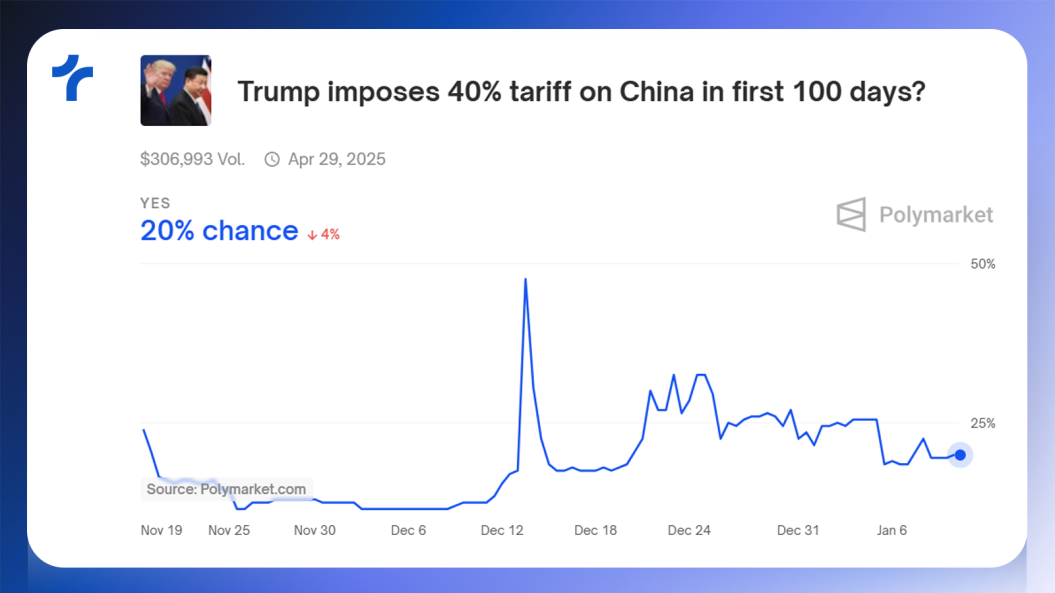
Another key issue involves import tariffs, particularly on goods from China, Mexico, and Canada.
While protectionist policies may offer certain advantages, they also carry the risk of increasing inflationary pressures.
The Republican platform itself highlighted protectionist measures as a priority for the U.S. economy.
The likelihood of imposing tariffs is higher for China compared to neighboring countries.
Bitcoin Reserve
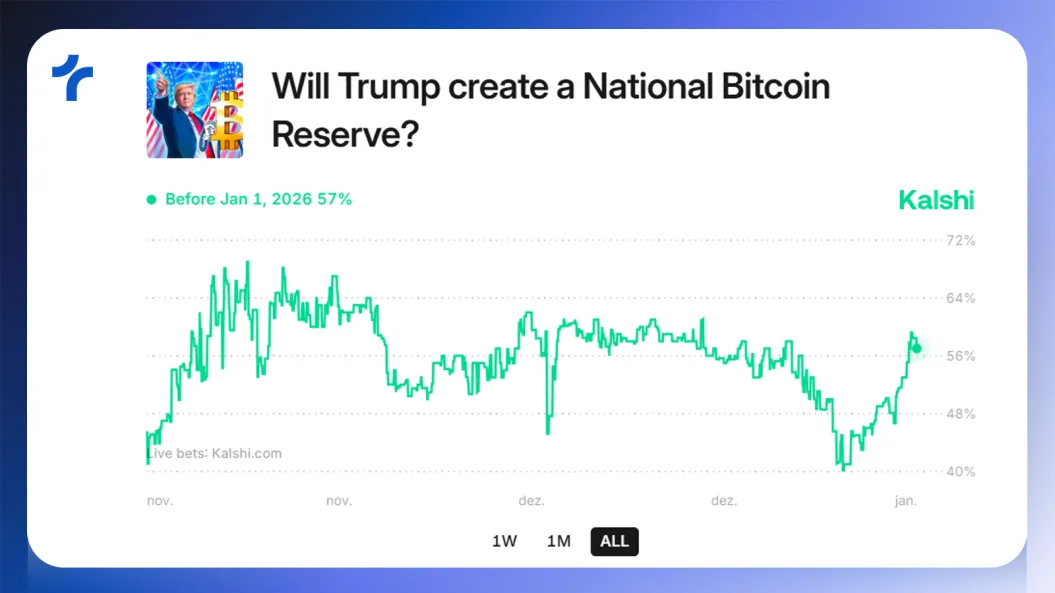
Another significant factor during the election was Trump's pro-crypto stance, along with that of many Republicans, leading the market to anticipate more flexible regulations.
Additionally, there is speculation about the potential creation of a national Bitcoin reserve, though its actual implementation remains uncertain.
According to Kalshi, the probability of such a reserve being established in 2025 is currently around 50%.
Final Thoughts
The outlook for 2025 is positive, though not exceptionally so. Experts anticipate GDP growth between 2% and 2.5%, while inflation is expected to range between 2% and 3%.
Additionally, a 75 to 100 basis point cut in the Fed Funds rate is projected, which could ease credit market conditions.
Asset markets show stronger expectations, with the S&P 500 expected to deliver a return of approximately 10%, and the NASDAQ potentially reaching 20% growth in 2025.
Gold is forecasted to see slower growth, while Bitcoin is expected to experience faster gains.
This is not investment advice but rather a compilation of estimates from influential individuals and institutions.
Controlling inflation and public debt is essential for sustained economic development.
Follow Truflation or visit our website for daily updated inflation data and to stay informed on the macroeconomic outlook.
Truflation Website | TRUF.Network | X | Linkedin | Discord | Telegram | Github| YouTube

